While Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and other 2.4 GHz technologies dominate short-range communication today, a wireless technology operating in lower frequency bands is carving out its own niche in the vast field of the Internet of Things (IoT) with its irreplaceable advantages. Sub-1GHz (Sub-G for short) wireless modules, much like an unobstructed "suburban expressway," stand in stark contrast to the congested “downtown urban highway" of the 2.4 GHz band, becoming a backbone for achieving wide-area IoT connectivity with their exceptional characteristics of long range and low power consumption.

-
Understanding Sub-G Modules
Sub-G modules, short for Sub-1 GHz modules, are wireless radio frequency modules that operate in license-free ISM frequency bands below 1 GHz (such as 169 MHz, 315 MHz, 433 MHz, 470 MHz, 868 MHz, 915 MHz, 920 MHz, etc.).
Their technical advantages are rooted in basic physics: The lower the frequency, the lower the propagation loss of the radio wave and the stronger its diffraction capability. This allows Sub-G modules to easily achieve kilometer-level communication distances and powerful wall-penetrating and obstacle-surpassing capabilities, making them particularly suitable for deployment in complex environments and IoT applications requiring large-scale coverage.
-
Network Topology Structures
Sub-G modules support flexible network architectures to adapt to ever-changing application scenarios.
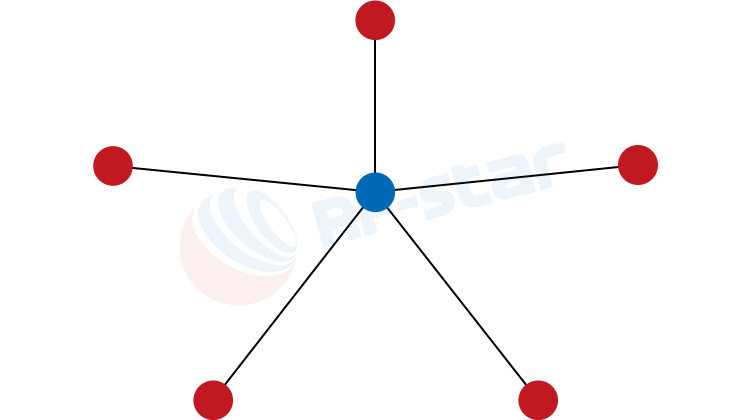
Star Topology: All end nodes communicate directly with a central gateway or concentrator. It features a simple structure and very low power consumption, making it the preferred choice for
LoRaWAN and many proprietary protocols, perfectly suited for large-scale applications like smart metering and environmental monitoring.
Point-to-Point Topology: Establishes a direct link between two devices. It is simple and direct, with low latency, often used for remote control and data transparent transmission.
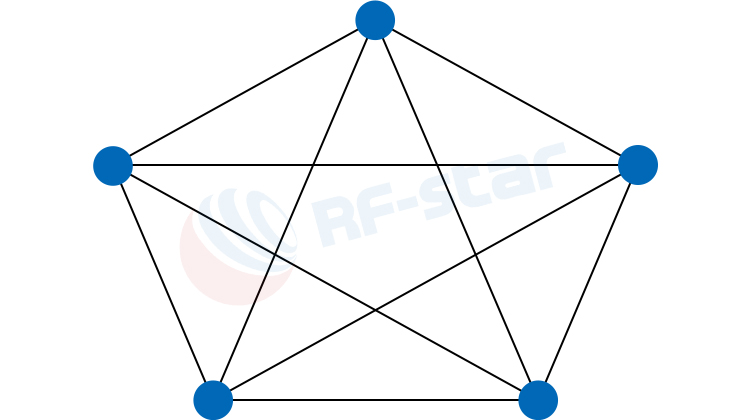
Mesh Topology: Each node can act as a relay, automatically forming a network and relaying data transmissions. This can greatly extend network coverage, suitable for areas where gateway deployment is difficult but wide coverage is needed.
-
Core RF Technologies and Chips
The implementation of Sub-G modules relies on their underlying chips and communication protocols, mainly divided into the following categories:
LoRa (Long Range Radio)
This is one of the most representative technologies. It uses Chirp Spread Spectrum (CSS) technology, achieving ultra-long-range communication with very low power consumption and possessing extremely high receiver sensitivity, significantly improving link budget and anti-interference capability.
Representative Chips: Semtech's SX1276, SX1262 series.
Proprietary Protocols (Private Protocols)
Chip manufacturers provide basic RF transceiver chips, based on which developers can customize private protocols. This approach offers controllable cost and high flexibility.
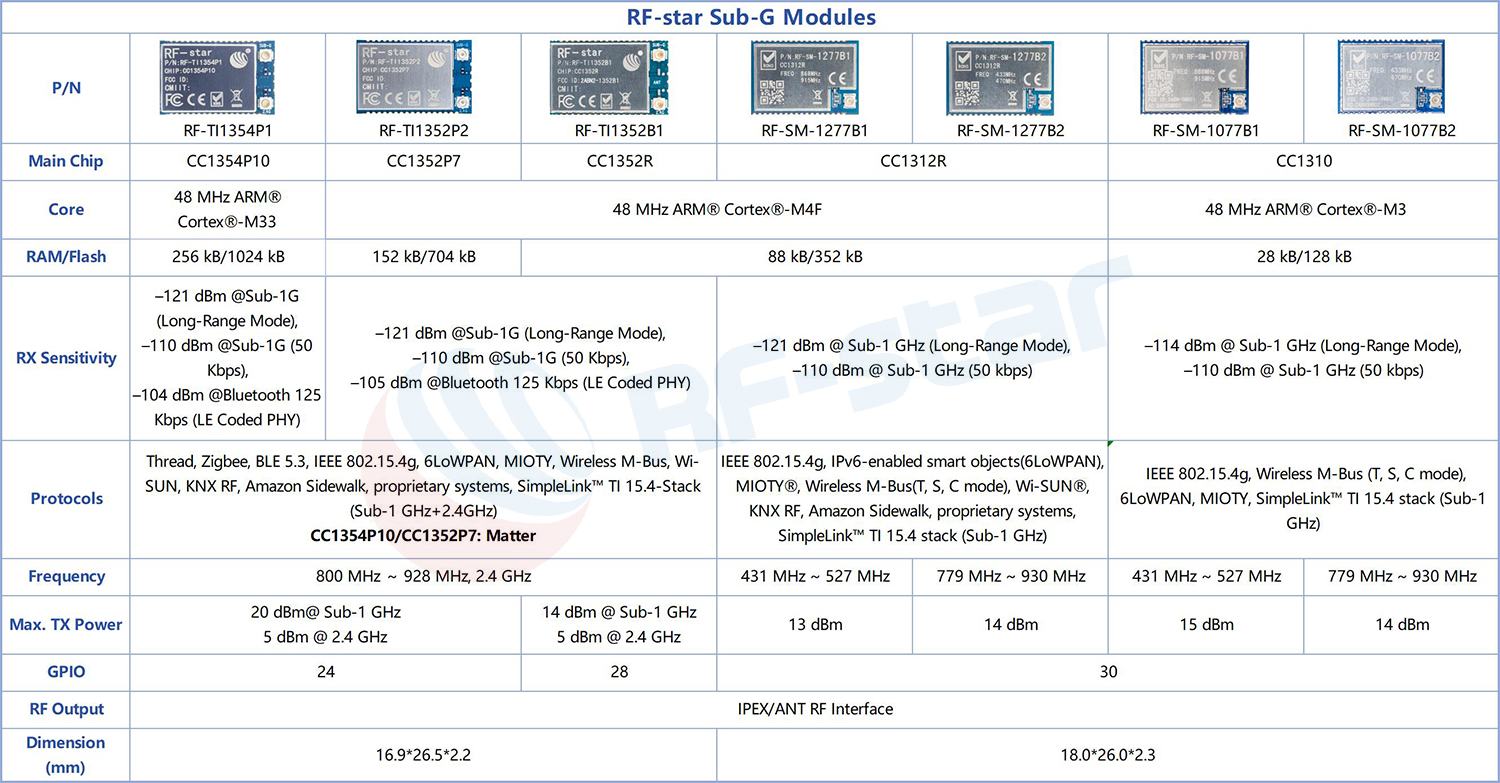
Representative Chips: Texas Instruments (TI)'s CC1310, CC1312R, CC1352R, CC1352P, CC1352P7, CC1354P10, Silicon Labs' Si446x series.
RF-star also supply the CC1310(RF-SM-1077B1/RF-SM-1077B2), CC1312R(RF-SM-1277B1/RF-SM-1277B2), CC1352R(RF-TI1352B1), CC1352P(RF-TI1352P1), CC1352P7(RF-TI1352P2) ,CC1354P10(RF-TI1354P1)
Wi-SUN (Wireless Smart Ubiquitous Network)
This is an open standard protocol based on IEEE 802.15.4g standards, renowned for its powerful mesh network self-forming and self-healing capabilities and high scalability. It is very suitable for IoT applications requiring large scale, high reliability, and frequent communication between devices, such as Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) and smart power distribution.
Representative Chips: TI's CC1312R, CC1352R, CC1352P, CC1352P7, CC1354P10 and other series chips, featuring +20 dBm transmit power, are an ideal hardware foundation for building Wi-SUN networks.
See RF-star’ Sub-G wireless modules list: CC1312R(RF-SM-1277B1/RF-SM-1277B2), CC1352R(RF-TI1352B1), CC1352P(RF-TI1352P1), CC1352P7(RF-TI1352P2), CC1354P10(RF-TI1354P1)

Other Standard Protocols
Including Sigfox (Ultra-Narrowband technology), wireless M-Bus (European standard for smart metering), Z-Wave (smart home protocol), etc., each playing an important role in specific application fields.

-
Core Characteristics of Sub-G Modules
Ultra-Long Transmission Distance: Under the same transmit power, its communication distance far exceeds that of 2.4 GHz technologies, easily covering ranges of several kilometers.
Powerful Penetration and Diffraction Capability: Low-frequency signals can effectively bypass or penetrate obstacles like buildings and vegetation, performing stably in complex environments.
Ultra-Low Power Consumption: Many protocols are optimized for battery power, combined with deep sleep modes, enabling device battery life to last for years or even over a decade.
Strong Anti-Interference Capability: The Sub-G band is far from crowded bands like Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, with low environmental noise, making communication links very reliable.
Large Network Capacity: Based on various network architectures like Star topology, a single gateway can connect to tens of thousands or even hundreds of thousands of end nodes, facilitating large-scale deployment.
Excellent Interoperability (Specifically for standard protocols like Wi-SUN): Adhering to globally unified open standards, devices from different manufacturers can seamlessly access the same network, breaking down ecosystem barriers.
-
Typical Application Scenarios
Smart Cities and Utilities: Including remote reading for smart water/electricity/gas meters, smart street light control, smart parking, and urban environmental monitoring, representing the most classic application area for Sub-G modules.
Smart Agriculture and Livestock Farming: Enabling field soil moisture monitoring, meteorological data collection, smart irrigation control, and livestock location tracking.
Industrial IoT (IIoT): Used in vast factory areas or mines for equipment condition monitoring, asset tracking, and pipeline safety monitoring.
Smart Home and Security: Providing whole-house stable coverage for devices like smart door locks, door/window sensors, and smoke detectors, with strong signal penetration. The Z-Wave protocol is widely used in overseas smart homes.

-
RF-star Sub-G Module Solutions
RF-star Technology provides a series of mature and stable Sub-G modules. Their advantages in hardware design and integration greatly help customers simplify the product development process.
Rich Package Designs
RF-star modules adopt standardized stamp-hole SMD packages with diverse sizes, making them very suitable for embedding into various structures. This integrated SMD package facilitates large-scale production using automated pick-and-place machines, effectively improving production efficiency and ensuring product consistency.
Flexible Antenna Options
To accommodate different product design needs, RF-Star's Sub-G modules offer various antenna connection methods. For devices requiring built-in antennas, the PCB antenna on the module is convenient and cost-effective. For applications requiring optimal RF performance, the module is equipped with a standard generation IPEX interface, allowing easy connection to external rod antennas or flexible antennas, providing engineers with maximum design flexibility.
Plug-and-Play Reliability
Choosing RF-Star Sub-G modules means developers do not need to invest high costs and effort into complex RF circuit design, and some modules also feature proprietary transparent transmission protocols. These critical and time-consuming steps have been completed on the module side, ensuring that end products can be brought to market quickly with excellent communication stability and reliability.
Rich Interface Support
RF-Star's Sub-G modules provide comprehensive hardware interface resources for easy system integration, including but not limited to UART, SPI, I2C, and other standard interfaces. The abundant interface resources meet the connection needs of most IoT nodes.
Multi-Protocol Compatible Platform
Some of RF-Star's Sub-G modules support dual-mode concurrent operation (2.4 GHz + Sub-G), and can also support various communication protocols such as Wi-SUN and proprietary protocols. The same hardware platform can adapt to different market and application requirements, also reserving ample space for future product upgrades and feature expansion.
In the current era of increasingly diversified IoT connectivity needs, Sub-G modules have become an indispensable part of wide-area IoT applications due to their comprehensive advantages in range, power consumption, penetration capability, and cost. The diverse, high-performance module solutions provided by RF-Star continue to empower developers, significantly lower the barrier to R&D, and drive the boundaries of the "Internet of Everything" to expand wider and deeper.