Ⅰ. What is a Bluetooth Low Energy Module?
Physical Composition: Bluetooth Low Energy Module = BLE chip + essential peripheral circuits (crystal, capacitors, etc.) + RF section (antenna matching circuit) + shielding cover (for interference prevention). This complete package allows you to use it immediately without dealing with complex RF design.
Simple Understanding: Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) is like an "energy-saving version" of classical Bluetooth – it's specifically designed for small, battery-powered devices that need to run for long periods. For example, your smart bracelet, electronic scale, or anti-loss tags all rely on BLE technology to maintain connections while allowing the battery to last for months or even years.
Module vs. Chip: How to Choose?
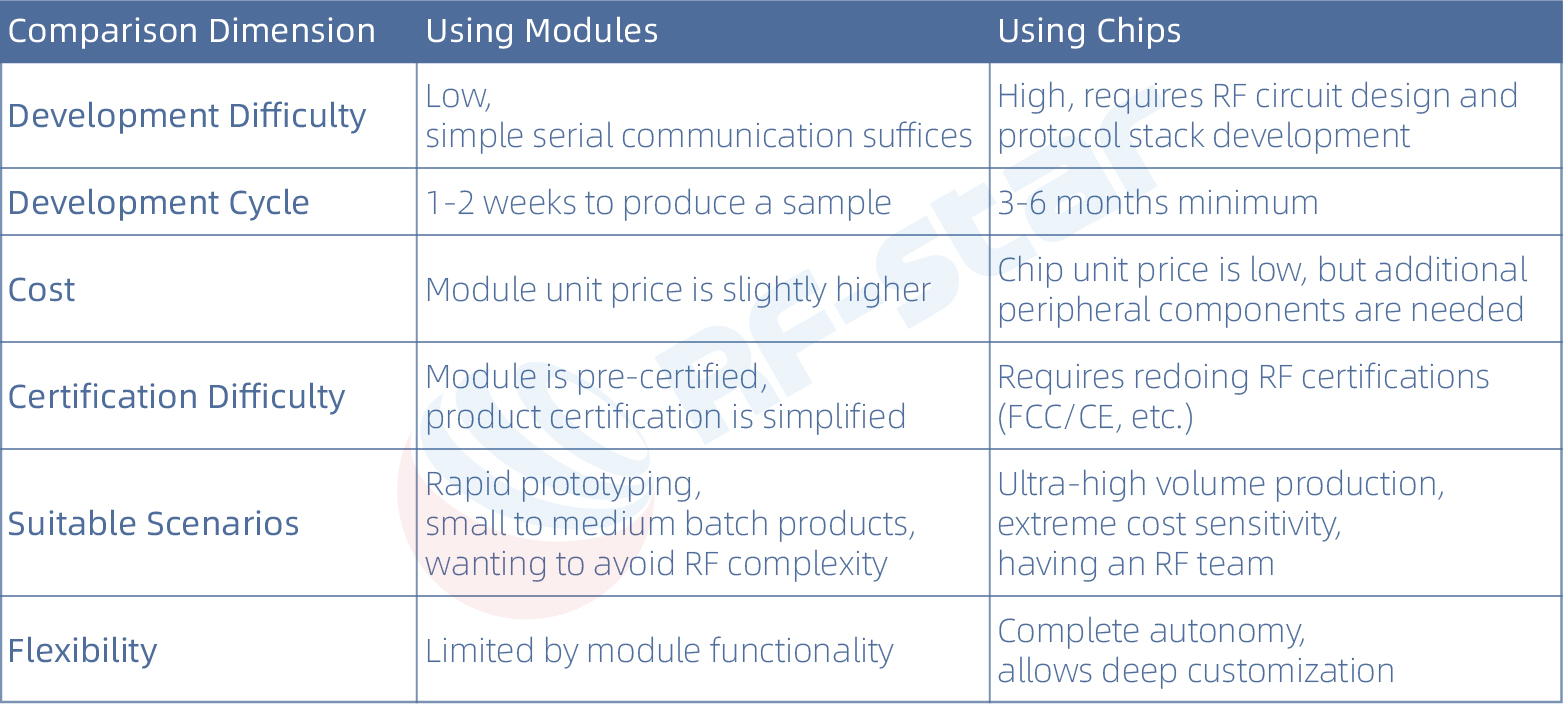
Suggestion: For 90% of IoT products, using a module is more cost-effective. The saved development time and certification costs far outweigh the price difference of the module.
Special Note: Common module certifications like FCC, IC, etc., require the module to include a complete RF circuit, shielding cover, and independent power supply. There are certain differences in whether a module's certification can be referenced depending on the region, the specific end product, and the chosen testing laboratory. To ensure smooth certification, RF-star recommends users directly communicate with the certification laboratory to confirm specific requirements.
Ⅱ. What are the main types of Low Power Bluetooth modules on the market?
1. Classified by Function
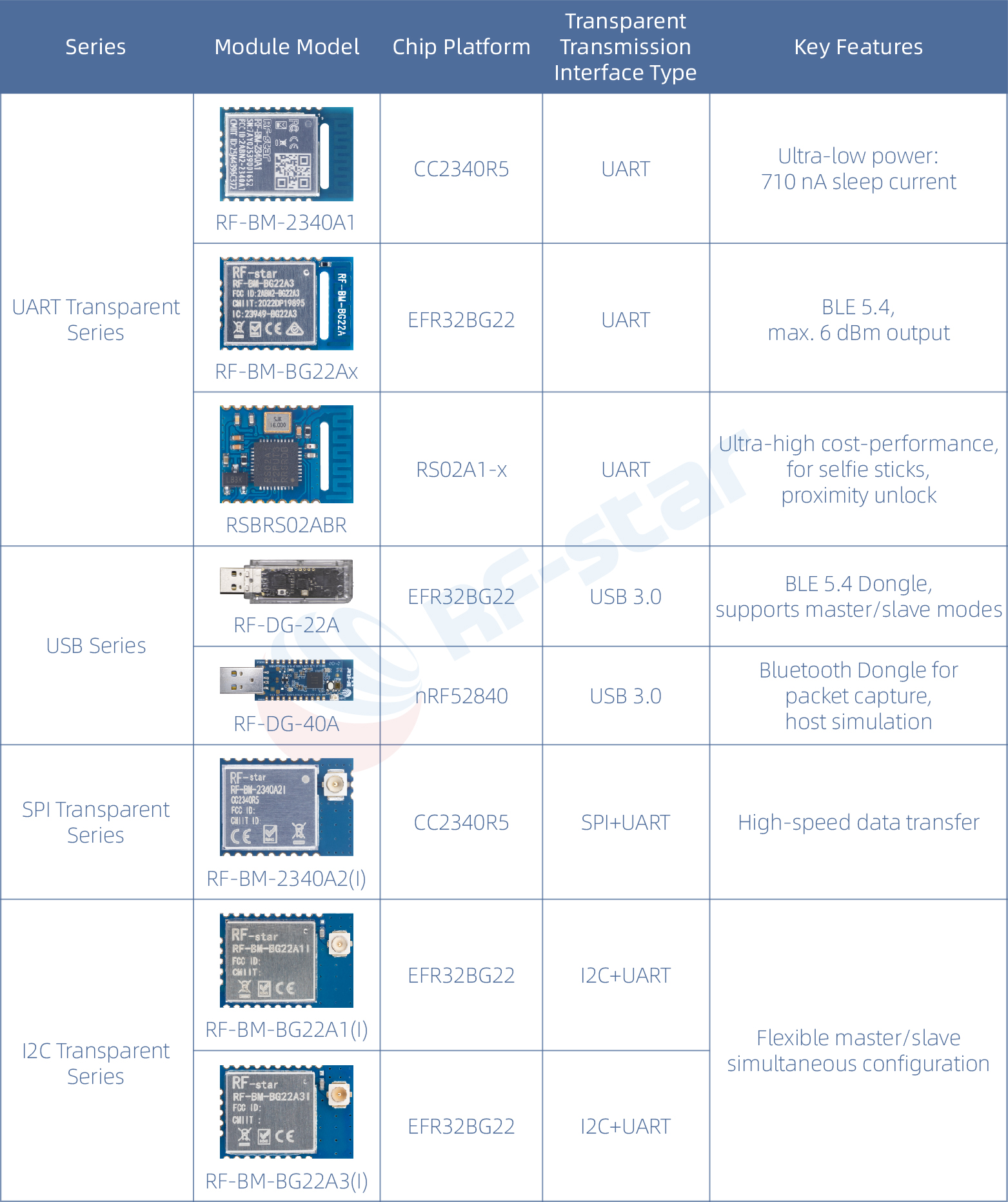
Transparent Transmission Module: The most commonly used, acts like a "data pipeline," transmitting data received via Bluetooth directly to the microcontroller. Users don't need to understand Bluetooth protocols, just wire it up and use it.
Controller Module: Has its own processing capability and can be programmed for logic. Customers can write their own programs to utilize the chip's internal core, potentially saving an external MCU and reducing costs. For example, the RF-star RF-BM-2340B1 uses the TI CC2340R5, which has a built-in ARM Cortex-M0+ core, and all GPIOs are brought out, allowing it to handle both Bluetooth communication and user applications.
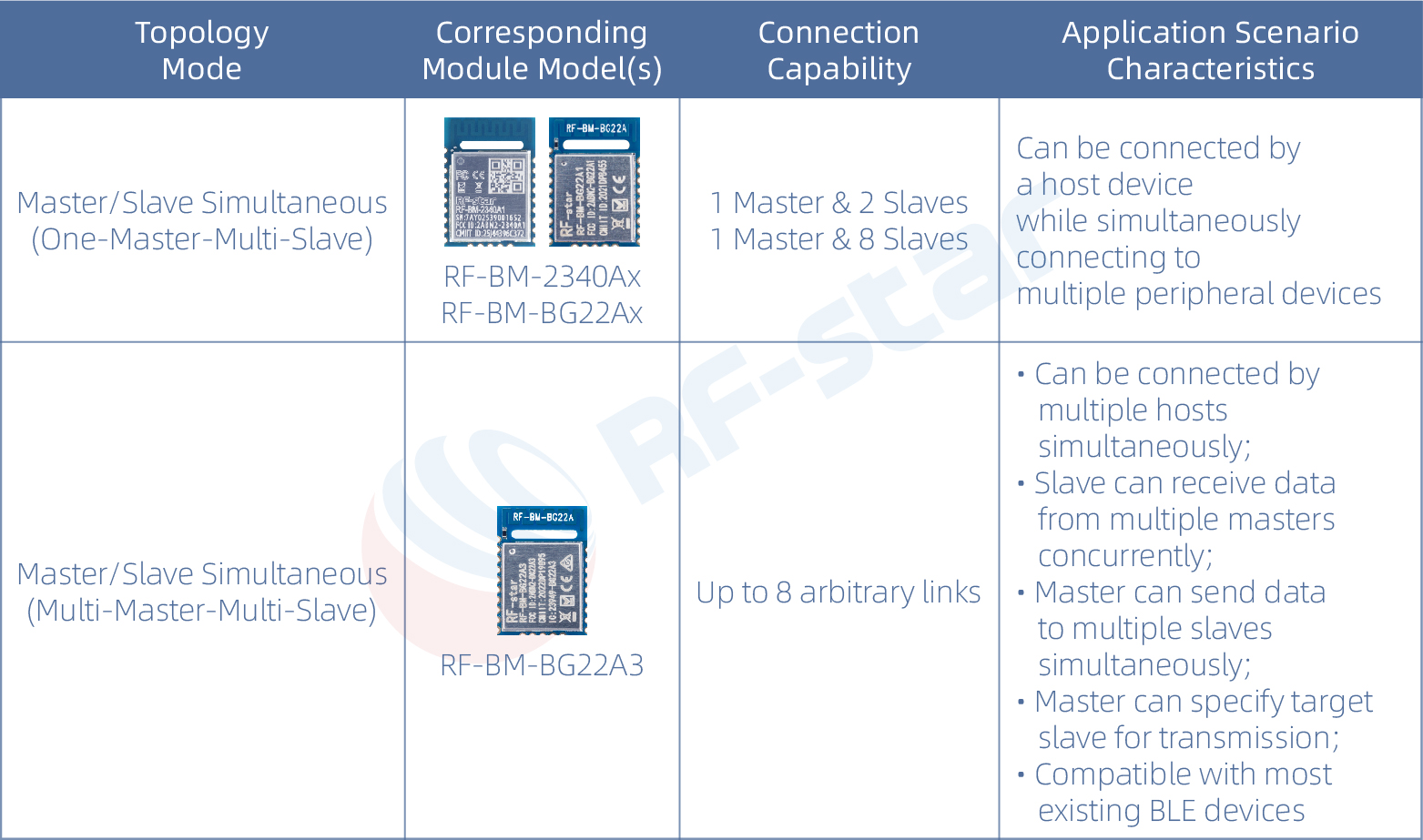
RF-star Modules Classified by Chip Platform
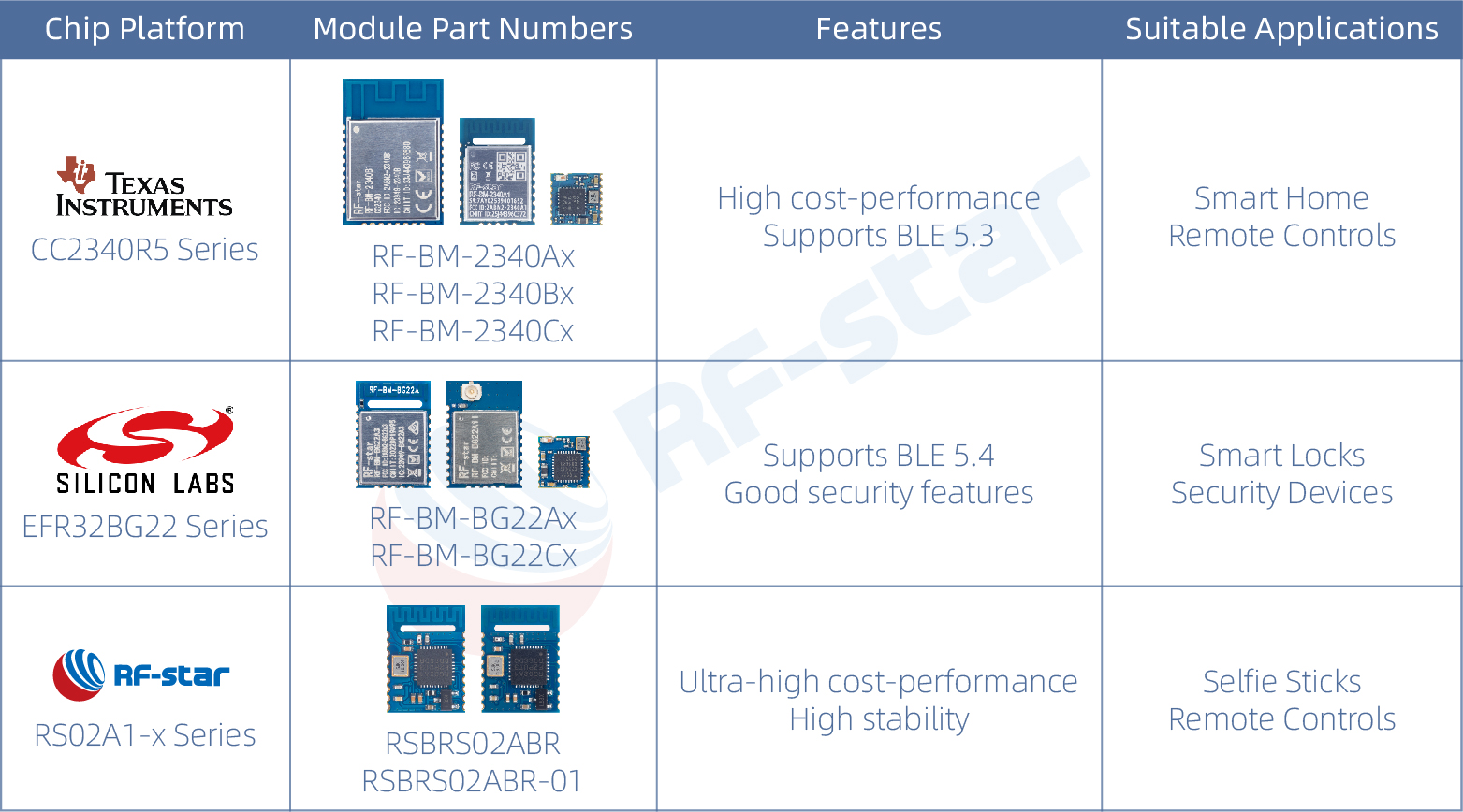
All the above modules can fulfill both transparent transmission and independent development needs.
Serial Port Type (UART): Easiest to get started with, connect and use, e.g., RF-star RF-BM-2340A1.
USB Type: Plug directly into a computer, no additional interface needed, customers develop their own PC software, e.g., RF-DG-22A.
SPI/I2C Type: Differences in serial transmission rates, e.g., RF-BM-2340A2 supports SPI transparent transmission protocol, RF-BM-BG22Ax supports I2C transparent transmission protocol.
Ⅲ. Quick Start: How to Use a BLE Transparent Transmission Module?
Wiring is Super Simple (Using RF-BM-2340A1 as an example)
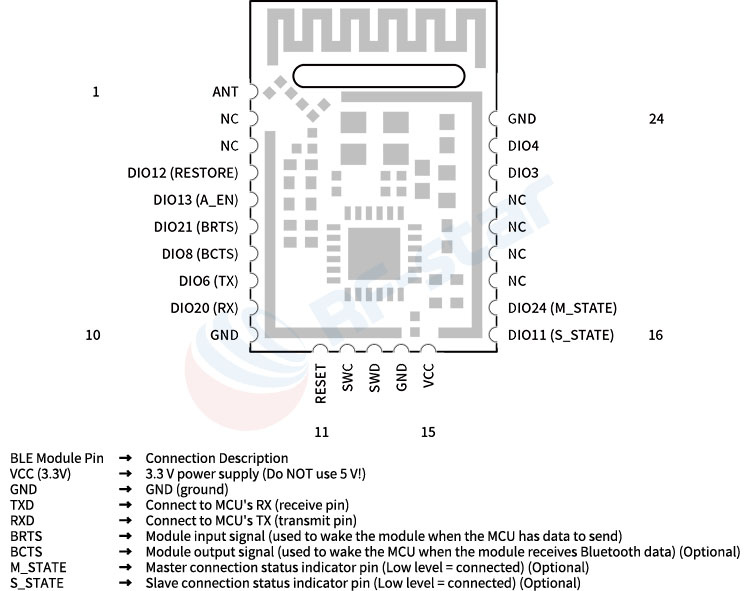
Note: TX connects to RX, RX connects to TX, don't reverse them! Flow control pins should be grounded if not used.
Power the module (3.3V, maximum current should not exceed module specifications)
Download a Bluetooth debugging app on your phone (Recommended "nRF Connect")
Search and connect to the module using the phone app (Default name is usually RFSTAR_XXXX)
RF-star Module Flow Control Method (RTS/CTS) (BRTS/BCTS):
Module RTS/BCTS → MCU CTS
Module CTS/BRTS ← MCU RTS
Applicable Modules: RF-BM-BG22A1, RF-BM-2340A1, RF-BM-4044Bx, etc.
Ⅳ. In-depth Analysis of Bluetooth Working Principles
Advertising ------ Peripheral Device Broadcasting
The peripheral device periodically "shouts": I'm here! My information is...
Advertising Packet Contains:
Device Name (e.g., "RFSTAR_BLE")Manufacturer-specific data
AT+POWER=0 // Modify transmit power to 0 dBm
The central device turns on its "ears," listening for who is advertising nearby:
Advertising packet content
Typical examples: Phones, tablets, gateways
Slave Device (Slave/Peripheral):
Advertises its presenceTypical examples: Sensors, bracelets, beacons

Master/Slave Combo (Central/Peripheral):
A device that combines both master and slave functions, such as:Smartwatch (Slave: connects to phone; Master: connects to headphones)

Bluetooth Gateway (Master: connects to multiple sensors; Slave: connected by phone for configuration)
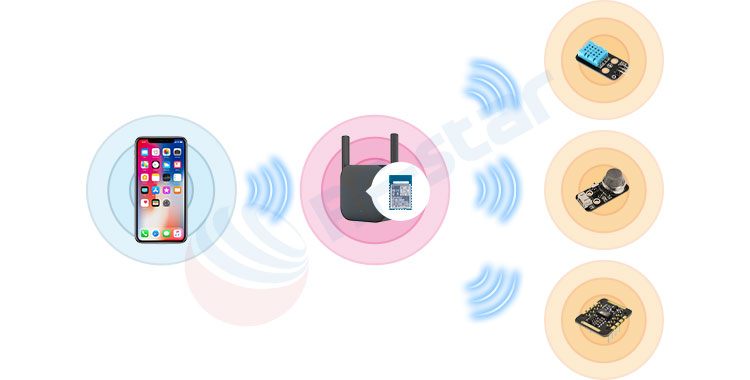
Modes Supported by RF-star Transparent Transmission Modules
Four Steps to Establish a Connection:
Step 1: Slave Device Advertising
↓
Step 2: Master Device Scans and Selects Target
↓
Step 3: Master Device Initiates Connection Request
↓
Step 4: Both Parties Negotiate Parameters → Connection Successful!
Connection Parameter Optimization Configuration
Connection Interval: Affects speed and power consumptionAT+CNT_INTERVAL=16,200 // Device current connection interval is 20 ms (16*1.25 ms), connection supervision timeout is 2000 ms
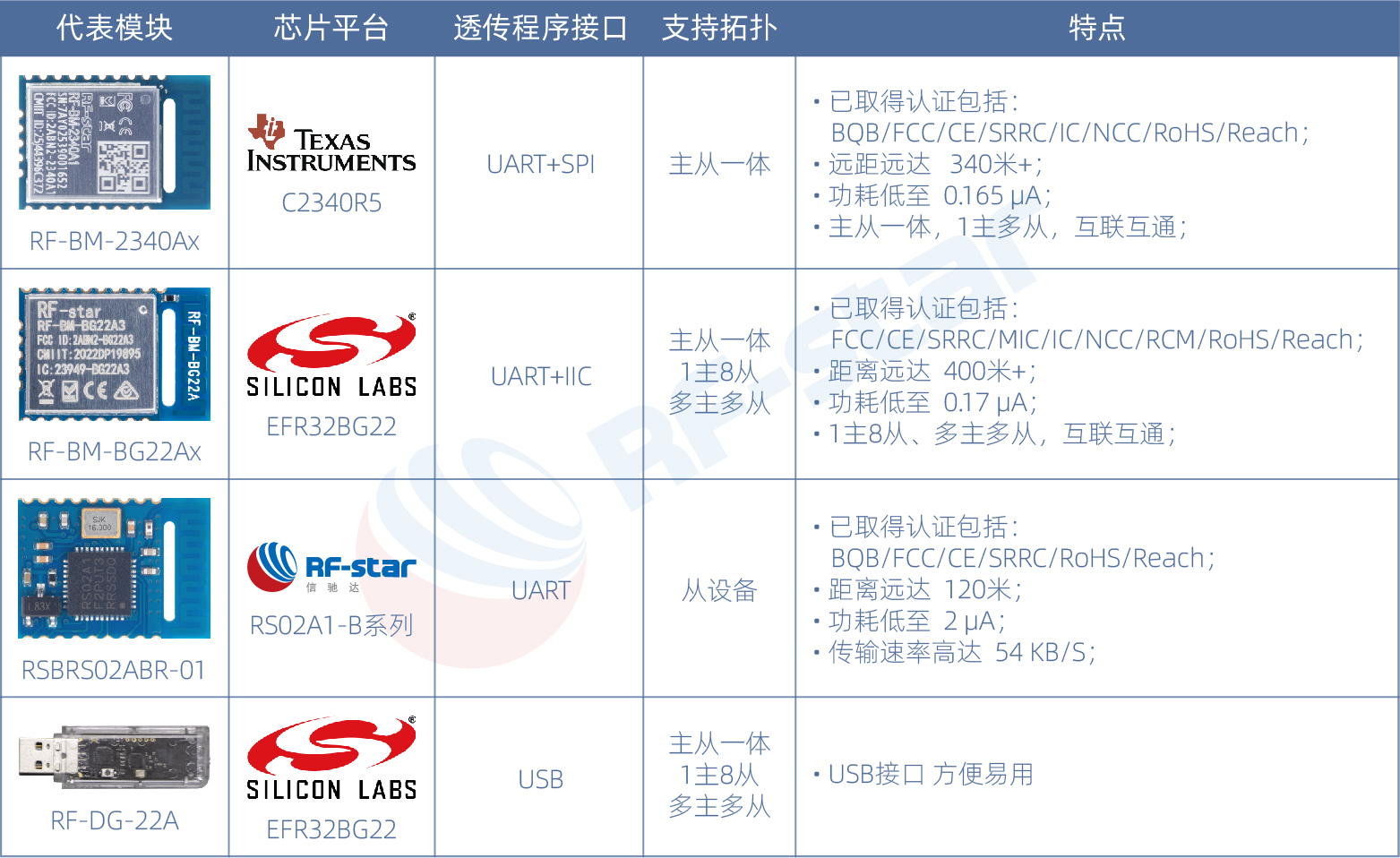
Ⅴ. RF-star Transparent Bluetooth Module Selection Table
Ⅵ. Common Problem Quick Reference
Q1: Can't find the module?
Check 1: Confirm if the module is in advertising mode (STATE pin can indicate)Check 4: Is the antenna intact, is the module inside a metal enclosure (signal shielding)?
Solution 4: Adjust the connection interval (intervals too small may be unstable)
Solution 4: Reduce the amount of data sent at once (send in packets)
Ⅶ. Try it out now!
Some DuPont wires

Remember: Using BLE transparent transmission modules isn't difficult; the key is to try, experiment, and learn from mistakes. Most problems stem from incorrect wiring, power supply, or mode settings. RF-star modules come with detailed technical documentation and example codes for some MCUs. When encountering problems:
Consult the module's transparent transmission protocol manual and development board manualContact technical support (info@szrfstar.com)